Public and Private Subnets, introduction

This is the first post of a series of 3 where we are going to go through the Basics of Subnetting in AWS where we will cover, in a very light way, the fundamentals of the subnets and how to set up them in Cloud Formation.
We have seen that AWS creates for us a space called VPC, Virtual Private Cloud where all our things are located.
A virtual private cloud (VPC) is a virtual network dedicated to your AWS account. It is logically isolated from other virtual networks in the AWS Cloud. You can launch your AWS resources, such as Amazon EC2 instances, into your VPC.
The VPC spans all the Availability zones of the Region where the VPC is created.
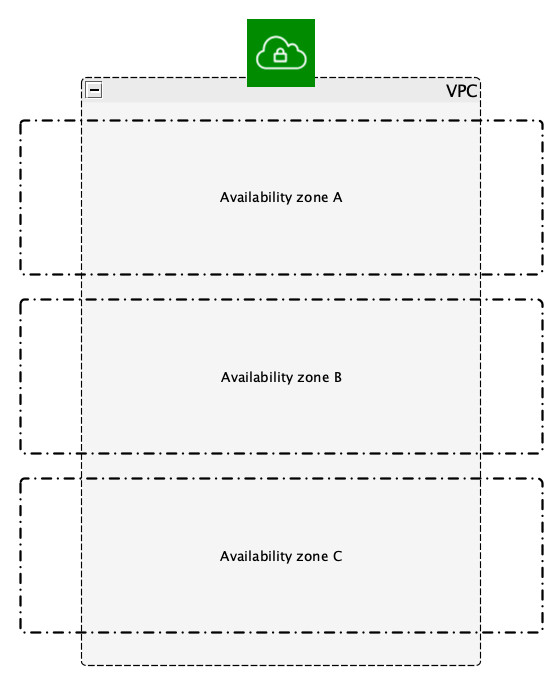 VPC: Virtual Private Cloud
VPC: Virtual Private Cloud
If you think about the VPC like a set of IP addresses then you can get a group of those addresses and create a special block, your Subnet. One interesting thing is that the Subnet needs to be defined in one Availability zone only.
This way you can distribute your Network, and each subnet contains different elements of your system.
Note You can have your stuff directly in the VPC, but it is recommended to split them into Subnets so you ca replicate along availability zones, control the access to certain components by setting a subnet as private or public…
And talking about Public and Private, if we go back to our previous post about CloudFormation we mentioned our will to have a Private Subnets and Public Subnets but we did not configure them anyhow.
Let us understand a bit better what that means:
- We call Public Subnet to a Subnet that has available access to the Internet from a network perspective, this means that the Subnet will be able to perform OUTBOUND calls to the Internet and receive INBOUND calls.
We can do several things to limit, for example, the INBOUND calls, via IP Whitelisting for example.
- A Private Subnet, on the other hand, is a Subnet that has no access to the Internet, it is Decoupled. Other Subnets in the VPC can access to it, and for that reason, they make a lot of sense, you can have for example your EC2 instances there, running without access from the Outerworld, you can have your Databases and even your Lambdas there.
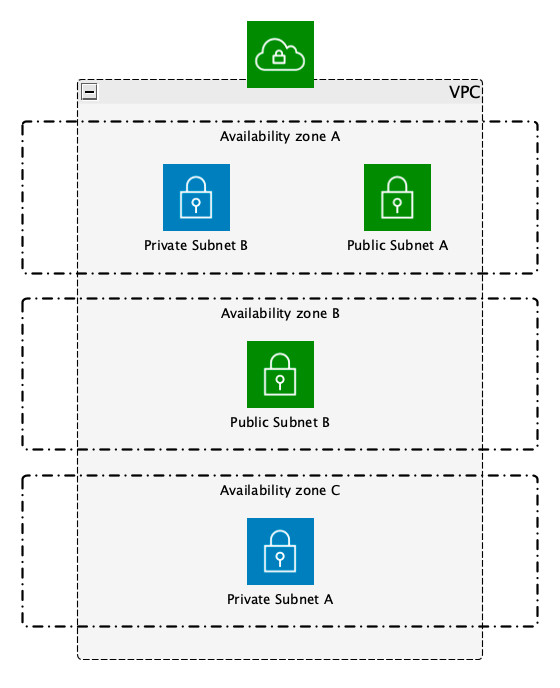 Subnets diagram
Subnets diagram
In the next posts, we will see how to set up Public and Private subnets, and also how to have some special hybrid between them: A Private Subnet with Internet Outbound capabilities.